TS 10th Class Social Important Questions 7th Lesson Settlements - Migration
1 Mark Questions
Question 1.
Write any one reason for international migration?
Answer:
Education and Employment are the main reasons for international migration.
Observe the graph below and answer the questions 2, 3.
Question 2.
Which social background people are migrating more?
Answer:
OBC are migrating more
Question 3.
What is the reason for short-term migration?
Answer:
The reason for short term migration ¡n rural areas is distress caused there
Question 4.
What do we have in a settlement?
Answer:
In a settlement, we have different kinds of activities - educational, warehouse, commercial, etc
Question 5.
Why were the early humans called hunter-gatherers?
Answer:
Early humans hunted and gathered their food. That is why they were called hunter-gatherers
Question 6.
The hunter-gatherers were nomads. Why?
Answer:
The hunter-gatherers were kept moving from place to place. This was in search of food gathering food from plants and trees and hunting animals for meat, hide, and other uses
Question 7.
What kinds of places attracted settlements?
Answer:
Some basic concepts are to be understood for this. Those are
- site
- situation and
- the history of the place
Question 8.
What does site refer to?
Answer:
Site refers to the characteristics of the place - its topography, altitude, water characteristics (does it have lakes, rivers, underground water, etc.), types of soils, security, shelter from natural forces and so on
Question 9.
Name any two cities whIch were developed by the colonial powers?
Answer:
Mumbai and Chennai
Question 10.
What is called Urbanisation?
Answer:
People have been increasingly taking up non-agriculture work and living in cities and towns. This is called Urbanisation
Question 11.
Name the their cities which accommodate more than 10 million people each?
Answer:
Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata
Question 12.
What are the problems in urbanisation?
Answer:
Though there has been an increase in urbanisation, the necessity of providing basic infrastructure that can support this growth is missing. e.g.: roads, drainage, electricity. waler and public facilities
Question 13.
What are aerotropolis?
Answer:A new kind of settlement is occurring in many countries, including India. These settlements around large airports are called Aerotropolis
Question 14.
What are the facilities in an aerotropolis?
Answer:
Hotels, shopping, entertainment, food, business conferencing, etc
Question 15.
What are the comforts of people in aerotropolis?
Answer:
People can tty in, conduct their business with their counterparts right there, and fly out- with all the contort of a city, without the traffic and other problems
Question 16.
Name some farm of aerotropolises which are emerging in India?
Answer:
- Bengaluru International Airport.
- Indira Gandhi International Airport - Delhi
- Rajiv Gandhi International Airport - Hyderabad
Question 17.
What are Megacities?
Answer:
The cities having more than 10 million persons are Megacities
Question 18.
What are Towns?
Answer:
All the urban areas having populations between 5000 to 1 Iakh are called Towns
Question 19.
What are Hamlets?
Answer:
A group of houses within the revenue village are called Hamlets
Question 20.
How does migration arise?
Answer:
Migration arises out of various social, economic or political reasons
Question 21.
How can we identify a person as a migrant?
Answer:
For identifying a person as a migrant, two criteria are used by the centres: birthplace last usual place of residence
Question 22.
What is the most common reason for female migration?
Answer:
Marriage is the most common reason for female migration
Question 23.
What is the most common reason for male migration?
Answer:
Employment or seeking employment is the most common reason for male migration
Question 24.
Give some other reasons for migration?
Answer:
Dissatisfaction with employment opportunities for studies, loss in business, family, friends, etc. are also some other reasons for migration
Question 25.
Where do the urban migrants have to work?
Answer:
Most urban migrants have to work in the unorganised sector. They could be working as hawkers, painters, repair persons, rickshaw puliera, construction labour, etc
Question 26.
Why do migrants continue to live as daily workers?
Answer:
The migrants from rural to urban are not able to find jobs in the organised sector and therefore theres no job security and decent income that they were aspiring for, They continue to live as daily workers
Question 27.
Why is the number of seasonal migrants underestimated in India?
Answer:
The number of seasonal migrants is underestimated in India due to limitations in the definition of the term migrant used n national surveys
Question 28.
Who are the rural seasonal migrants?
Answer:
The rural seasonal migrants are mainly agricultural labourers or marginal farmers in their place of origin and mostly belong to low-income households. Dalits and Adivasis
Question 29.
Where do rural seasonal migrants work?
Answer:
The rural seasonal migrants work in agriculture and plantations, brick kilns queens, construction sites and fish processing
Question 30.
Who have a long history of migrating?
Answer:
Maie from Saora tribals have a long history of migrating to work in Assam plantation, Munda and Santhal men migrate to work in mining sites in Odisha
Question 31.
Which depend on migrant workers?
Answer:
Construction sites ¡n most urban areas depend on migrant workers
Question 32.
It Is also common to see migrants What is it?
Answer:
It is also common to see migrants selling plastic goods, vegetables, and engage in their petty businesses and casual labour
Question 33.
What is the economic condition of the seasonal migrants?
Answer:
Seasonal migrants are not only poor but have little or no land at their native place
Question 34.
What did the N.C.R.L find?
Answer:
The National Commission of Rural Labour in its reports in 1990s found that uneven development and regional disparity triggered and accelerated seasonal migration
Question 35.
How do the migrant labourers spend?
Answer:
Migrant labourers spend more on food as they cannot get food grains from fair-price shops at their workplaces
Question 36.
Why do they suffer from health problems?
Answer:
As they live in harsh circumstances and in unhygienic conditions, they suffer from health problems and are prone to diseases
Question 37.
Name some health problems from which they suffer?
Answer:
Bodyache, sunstroke, skin irritation and lung diseases
Question 38.
Why are migrants not able to access various health and family care programmes?
Answer:
Migrants are not able to access various health and family care programmes as they do not belong to the organised sector
Question 39.
Do the migrant workers have maternity leave?
Answer:
No, they do not have maternity leave
Question 40.
Which leaves a deep impact on migrants?
Answer:
Exposure to different environment, stress associated with it, food available and social atmosphere leave a deep impact on migrants
Question 41.
What does migration allow?
Answer:
Migration allows households to meet debt and other obligations without having to sell assets. It is also common to find migrant families buying house, land, agricultural machinery and consumer durables
Question 42.
How many kinds of migrations are there? What are they?
Answer:
There are two kinds of migrations. They are :
- InternaI migrations
- International migrations
Question 43.
How do some migrants migrate regularly?
Answer:
Some migrants might take up robs in the destination, acquire skills required in the destination area, become aware of how to get regular jobs and migrate regularly or permanently
Question 44.
Where do the skilled Indians migrate?
Answer:
The skilled Indians migrate to the U.S.A.. the U.K., Canada, Germany, Norway, Japan
and Malaysia
Question 45.
What is the; second type of international migration?
Answer:
The second type of international migration is unskilled and semi-skilled workers migrating to oil-exporting countries of the West Asia on temporary contracts
Question 46.
What is the Emigration Act, 1983?
Answer:
The Emigration Act, 1983 is the Indian law governing migration and employment of
Indians abroad
Question 47.
What do you suggest to overcome the problems of foreign migrants?
Answer:
The foreign migrants should take many necessary steps. They should opt proper inter mediaries for selecting jobs. Agreements should be written properly with legal aid
2 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Delhi is the second biggest city In the country. Explain the reasons for It?
Answer:
- The city of Delhi can claim to have been central to many empires that ruled India
- When India gained independence, the city remained Its capital
- Over the decades, the city has attracted people from all parts of India as they migrated in search of livelihood, jobs, etc.
- As the capital of the country, with the Parliament and Central Government offices, there are people from all parts living In the city
- Surrounding areas of Delhi are developed
- Establishment of industries in surrounding areas of Delhi
Question 2.
What are the reasons for migration?
Answer:
- Migrations can happen due to many reasons
- Females reported management as the most common reason
- Mates migrate on employment or seeking employment opportunities
- Dissatisfaction with employment opportunities In the native place is one reason
- SetIer opportunity for studies, loss in business, family feuds are some other reasons for migration
Question 3.
Create a pamphlet on "Prevention of Migration"?
Answer:
Prevention Of Migration
Reasons: When families migrate, they live in harsh circumstances and in unhygienic conditions, they suffer from health problems and are prone to diseases. Migratory pressures on communities of origin can be related to social and economic distress. They can be linked to environmental degradation as we as natural man-made hazards and they can be due to persecution on conflict and violence. By supporting disaster preparedness and building resilience at a community level.
Conclusion: We should prevent migration to reduce the above problems. National societies are contributing elevating pressures that can induce people to migrate against their will and desire
Question 4.
Analyse the problems of Urbanisation?
Answer:
Urbanization: The migration of people from rural areas to urban areas is called urbanisation
Causes of urbanisation:
- Natural growth
- Inclusion of rural areas and
- Migrations
Challenges of urbanisation:
- The rapid inflows of rural population to urban places give rise to housing problem and thus slums are developed in these places
- The decrease in rural population effects the agricultural protection due to shortage of workers In rural areas
- Due to use of more vehicles, air, water, sound pollutions are increased
- Traffic problems will arise
- Proper drainage facilities are not expanded
- Using of plastic covers is increased
- The unerrçloyment increases in urban areas
- Due to this, various criminal activities, corruption, etc. increase affecting the law and order system
Question 5.
How does the gender bias effect when the women work outside of the home now a days?
Answer:
Before the rise of large-scale industrialization, home and workplace were one and the same. But now the disparity between men and women in the workplaces is a common Issue.
Workers acknowledge gender dlscrimination is possible in modem organizations, but at the same time maintain their workplaces to be gender neutral. Women are facing a high degree of gender bias when it comes to their careers. There is a general perception that women are less capable than men Ni matters of business and decision-making
it Is often a strenuous struggle for a woman not just to her mettle but also to make a deserving way to the top. Career goals of women are considered less Important compared to male counterparts. The disparity is also seen in the wages and salaries also. Thus the relationship is negative
Question 6.
Write a brief note on Seasonal migration?
Answer:
Brief note on Seasonal Migration:
A large section of rural workers migrates for a short period in some specific seasons.
This duration may be less than six months.
Agricultural labourers, marginal farmers and adivasis are mainly seasonal migrants.
Examples for seasonal migration are sugar cane cutters, labourers Ni brick kiins
Question 7.
What happened as population increased?
Answer:
As population increased, there was more specialization weavers, potters, metal workers and other professions emerged. The number and variety of goods produced Increased and so did the trade in them. Rulers began to encourage craftspersons to settle in urban areas. Urban settlements, i.e., towns where people did not work in agriculture expanded
Question 8.
What do you know about Visakhapatnam?
Answer:
Visakhapatnam has a long history. It was ruled by different dynasties during pre-colonial Irnos. During the 19th century, the British and French fought a naval battle over this city. Coastal places were of immense significance for colonial powers because they could build poils there. These ports would enable the export of raw retenaIs to the coloniznig country
Question 9.
What happened In early settlement periods? Give an example?
Answer:
In early settlement periods, places which had favourable water supply and good protection from invasions were preferred. For example. Chhatrapati Sivaji built a foil in Pratapgad. Maharashtra, This site was chosen because of its altitude from where all the surrounding areas could be seen. This provided military security
Question 10.
Why did most of the population increase In cities and towns take place?
Answer:
Most of the population increase in cities and towns took place as a consequence of natural growth within the urban areas. Some of the growth in urban settlements took place by expansion, with the inclusion of rural areas surrounding older cities and towns. Only One-fifth of the growth is due to rural-to-urban migration
Question 11.
Why has the population of Visakhapatnam grown significantly over the centuries?
Answer:
Over the decades, Visakhapatnarns population has grown significantly. This growth is a result of the importance of Visakhapatnam as a port city. This population increase also indicates growth in economic and social opportunities
Question 12.
Why did the settlements become more and more complex?
Answer:
As settlements became more and more diversified in their characteristics, they also became more and more complex. Gradually, a network of places in a hierarchy has been formed
Question 13.
How does urban India contribute to Indians economic development?
Answer:
Service sector activities such as finance, insurance, real estate and business-related service activities such as transport, storage and communication contribute more than industrial activities. There Is no major growth of Industrial output over the last few decades
Question 14.
Give some examples of emerging aerotropolises. (International)?
Answer:
- Suvarnabhumi International Airport (Bangkok. Thailand)
- Dubai International ANport (Dubai, UAE)
- Cairo International Airport (Cairo. Egypt)
- London Heathrow Airport (London, UK)
Question 15.
Write down some problems of urbanization?
Answer:
- The growing urban population has to be housed
- It needs water supply, sewage and other waste disposals, transportation and many other things
- Vehicle use increases
Question 16.
Though there has been an morcase in urbanzation, the necessity of providing ultrastructure that can support this growth is missing. What is your opinion on the conditions of urban poor people?
Answer:
Due to urbanisation, the people of surrounding villages are reaching the towns and cities. Many of them aro working in unorganised sector. As they are economically backward, they are settling in slum areas.
Usually, they are occupying government unorganised (poram bok) areas for their residences. Govt also building colonies toi them.
Ex: Vambey Colony
But the slum areas in which they are Moving are lack of water, sanitation and toilet facilities. Mostly they are living in ill-healthy conditions
Question 17.
Why are Embassies set up?
Answer:
Embassies set up by the Indian Government in different countries are expected to follow the legal procedures and protect the welfare of the international migrants as given In the
Emigration Act
Question 18.
Which depends upon the needs of rural family members?
Answer:
Remittances - money sent by migrants from their destinations - are an important means of supplementing, or generating additional incomes for the rural family. The amount of remittances and the pressure to remain In the urban areas depends upon the needs of rural family members
Question 19.
Why do migrants retain the economic ties In rural areas?
Answer:
Migrants retain the economic ties in rural areas because they want to safeguard their rights over land and homestead. Families left in rural areas are important for most urban migrants. In fact, it is the family which decides whether their family monther should migrate or not
Question 20.
Why do people migrate from rural areas?
Answer:
People migrate from rural areas mainly due to insufficient employment opportunities, Inadequate income available in rural employment. They also migrate with the expectation of higher incomes and more opportunities for family mentors and may be better, services
Question 21.
Why do many families have residences at both the ends?
Answer:
Many families have residences both at their origin- (native place) and at the destination. They shift between the two depending on work and seasons. Migration does not necessarily involve the movement of all members of the family, and often the wife remains in the rural area
Question 22.
Why do migrants also pass on the urban opportunities to the rural areas?
Answer:
Migrants also pass on ttie urban opportunities to the rural areas so that potential migrants can engage in rural-based ob search. In most cases, migration is the survival strategy for many families
Question 23.
Do you think migrants are troublemakers? Justify your answer?
Answer:
- Yes. I think migrants are troublemakers
- The migrants may not be provided proper facilities by the government
- The migrants may question for proper facilities in the long course
- If the migrants begin to fight for their identity, then the trouble will start
Ex: Tamil people in Sri Lanka
(OR)
- No. I think migrants are not trouble makers
- Generally, migrants go for their livelihood
- Therefore no scope to tight for domination
- Migrants wont trouble anybody because they wont fight for identity and domination
Ex: Sugarcane cutters in Maharashtra
Question 24.
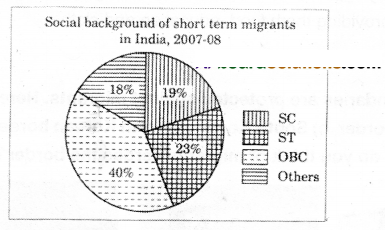
Graph: Social Background of short-term migrants in India. 2007-08.
 Read the above Pie diagram and answer the following questions?
Read the above Pie diagram and answer the following questions?
Question 1. How much per cent of STs migrated in 2007-08?
Answer:
STs constitute 23% of the migrated .n 2007 - 08
Question 2. Which is the maximum migrated class in 2007-08? What is Its percentage?
Answer:
The maximum migration is from the class of OBCs and it is 40%
Question 3. In which class we notice minimum migrants?
Answer:
The minimum migrants are there from others which is 18%
4 Marks Questions
Question 1.
Mention the challenges of Urbanization and suggest remedies?
Answer:
Urbanisation: The migration of people from rural areas to urban areas is called urbanisation
Causes of urbanisation:
- Natural growth
- Inclusion of rural areas and
- Migrations
Challenges of urbanisation:
- The rapid inflows of rural population to urban places give rise to housing problems and thus slums are developed in these places
- The decrease in rural population effects the agricultural production dueto shortage of workers in rural areas
- Due to use of more vehicles, air, water, sound pollution are increased
- Traffic problem will use
- Proper drainage facikties are not expanded
- Using of plastic covers are increased
- The unemployment increases in urban areas
- Due to this, various criminal activities, corruption, etc. increase affecting the law and order system
Remedies:
- Controlling of migrations from villages to towns and cities
- RecyclIng of waste materials
- Providing more employment opportunities in villages
- Eradicating the use of plastic
Question 2.
Write your reflections on the vulnerable conditions of Indian migrants to West Asia?
Answer:
Vulnerable conditions of Indian migrants to West Asia
- At times, migrant workers are not paid their salaries, and recruitment agents cheat prospective workers or collect more than the prescribed fees for their role in getting work for workers abroad
- Employers also terminate the job contract before its expiry, and change the employment contract to the disadvantage of migrant workers
- Pay less than the agreed salary and freeze fringe benefits and other perks
- They often force workers to do overtime without making additional payments and deny permission to keep ones own passport
- Indian migrant workers seldom lodge any complaint against their foreign employers for the fear of losing their jobs
Question 3.
Give solutions to address the urbanization problems?
Answer:
- Proper- maintenance of sewage water
- Proper supply of drinking water
- Providing infrastructural facilities in rural areas
- Giving importance to AicuIture
- Establishing industries in rural areas to generate employment
- Widening of urban roads
- Strict implementation of rules to reduce pollution
- Coordination among different wings or departments
Question 4.
Write down the advantages and disadvantages of the people when they migrate?
Answer:
Advantages:
- Urban migrants have plenty of opportunities for education and acquire new skills and take new jobs effectively
- Thus they earn more incomes
- Remittances are an important means of supplementing or generating additional income for the rural families
- Migration allows households to meet debt and other obligations without having lo sell assets
- Migrant families buy houses, land, gold, agricultural machinery and consumer durables
- Majority of migrants either remit or bring back savings
- Thus their purchasing power Increases
Disadvantages:
- Migrant labourers spend more on food as they cannot get food grains frown fair-price shops
- They live in harsh circumstances and in unhygienic conditions
- They suffer from health problems and are prone to diseases,
- They do not have creche facilities
- Grown children are not able to continue their studies at the parents new workplaces
- Exposure to different environments, stress associated with it, food availability and social atmosphere leave a deep impact on migrants
Question 5.
Read the given paragraph and interpret.
Labour being the most abundant factor of production, it would be ideal if the new ways of fanning used mud, more labour. Unfortunately, such a thing has not happened The use of labour on farms Is limited. The labour, looking for opportunities its thus migrating to neighbouring villages, towns and cities. Some labour has entered the non-farm sector in the village?
Answer:
- Labour means people who do the work either highly trained and educated or who can do manual work
- Each worker is providing the necessary labour for production
- Skilled or seniskiled or unslolled Labour . all are providing labour for production
- Thus labour is an essential item in production
Conclusion: II government provide loans to landless labour for Agriculture purpose, motor purposes, engines, etc. more labour we will find In the agricultural sector
Question 6.
What kind of places are attracted as settlements? Explain?
Answer:
Some places attract more people. There are many reasons for it. Some of them are:
- Good transport facilitIes: These facilities reduce the journey time. Hence a place which has good transport facilities attract the people more
- Good living conditions: One cannot change his own environment. The place which has good sanitation. Public transport system. Pollution-free environment naturally attracts more people
- Education, bob opportunities: Having good education gives a chance to take a good profession. The places which have good educational institutions and companies attract more people
Other reasons: Availability of good health services, having basic needs like electricity, peaceful lifestyle are some of the other factors contributing to attracting people
Question 7.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on it.
As population increased There was more specialization-weavers, potters workers and other prolesskwis emerged. The number and variety o goods produced increased and so did the trade in Them. Rulers began to encourage craftspersons to settle in urban areas. Urban settlements i.e. towns, where people did not practice agriculture expanded?
Answer:
At the beginning the rulers encouraged the craftspersons to settle in urban area. Gradually the facilities increased in urban areas. People who did not have land migrated to towns and cities to improve their living conditions. When industries were established, they left Their occupations and joined in industries for better lite.
Slowly town areas are increasing. The population is also increasing and the number of people who depend on agriculture are also slowly decreasing. The share of agriculture in GDP is also reducing. But In urban areas the people are facing so many problems
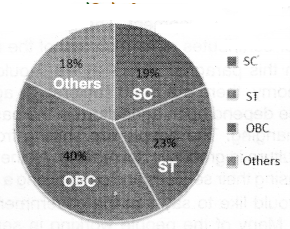
Question 8.
Observe the given pie chart and answer the question that follows:
The social background of shod-term migrants In India, 2007 - 08
 Write a paragraph analyzing It?
Write a paragraph analyzing It?
Answer:
This pie chart is about the social background of short-term migrants in India. 2007-08. It gives category-wise information of SC, ST, OBC and Others. On the overall observation, it is deafly understood that major number is from OBCa and others are less in percentage.
Normally in population, the number of people from other backward classes is more. It is also observed in rural areas. People belonging to scheduled castes and scheduled tribes have very less land and Nl some cases they have no lands. Recently the trend is changing. Due to some welfare schemes, they are also leading better life
The percentage of others is also nearly equal to the scheduled castes. Their migration purpose may be
different. Many of these migrants work In unorganized sectors like, construction work, brick industries, selling plastic goods and vegetables or in casual work.
The government should take care of these migrants and think why these people are migrating from their places. Impossible rural prosperity is to be focused. Public facilities are to be provided at the rural areas and so this migration can be stopped or decreased
Question 9.
How were the settlements begun and explain, why do they change?
Answer:
Settlements: For about 1.8 lakh years. early humans lived In bands as hunter-gatherers. They didnt practice agriculture. However, owing to changes in ways of obtaining food some bands took to the deliberate method of production of food agriculture.
The basic concepts of settlements are site, situation and history of the place. With regard to site of a place, its topography, altitude, lakes, rivers, type of soil, security, shelter and so on will be observed. Places do not exist In isolation. Elevated places are useful to see the surroundings if anybody is approaching can be identified easily. The historical background is also an important one for people to decide to reside there
For the sake of livelihoods and migration, settlements change. Delhi was the capital for many dynasties for many years. People do not want to stay at their places in rural areas. The people suffer a lot at rural areas because of distress in agriculture. The farmers also want to send their children to cities and towns for the sake of education and employment.
Sometimes the rural people migrate to urban areas for livelihoods, jobs, or to settle in any constructive work Many people in cities and towns choose self-employed we can Because of these reasons settlements have been changing
Question 10.
Observe the information given In the table and analyse.
Table: Migrations in India [Census 1991-2001]?
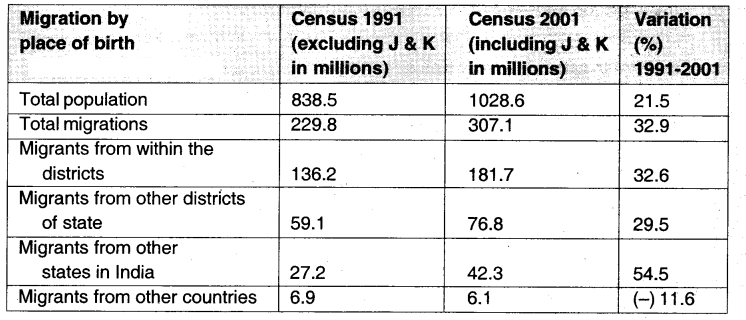
Answer:
Table Analysis:
According to 1991 & 2001 census
- Total population in 1991 was 838.5 millions excluding J & K. At the same time En 2001 it was 1028.6 millions including J&K. There was a vanation of 21.5% growth in the population
- Total migrated people in 1991 were 229.8 millions and they were En 2001,307.1 million. There was 32.9% variation from 1991 to 2001
- Migrants from within the districts in 1991 were 136.2 millions and in 2001 were 181.7 millions. The variation is 32.6%
- Migrants from other districts of state in 1991 were only 59.1 millions and in 2001 were 76.8 millions. The variation is 29.5%
- In 1991 migrants from other states in India were 272 millions and 2001 they were 42.3 million. The variation is 54.5%
- Migrants from other countries were 6.9 millions in 1991. This number reduced to 6.1 millions in 2001. Hence, the variation is (-) 11.6%
From the above information, it is evident that total migrations increased from 1991 to 2001. Migrants within the district and migrants from other districts of state increased. Because of employment, facilities and education also increased Some areas are not developed, thats why people are migrating from one place to other places
Conclusion: Finally from the above information we understand that migrants from other countries to India decreased. So we understand that foreigners are not preferring to migrate India because of lack of resources and employment arid low paid salaries
Question 11.
Read the paragraph and write your opinion.
Most of the population increase in cities and towns took place as a consequence of natural growth within the urban areas. The population of these urban areas increased over time. Some of the growth in urban settlements took place by expansion, with the inclusion of rural areas surrounding older cities and towns. Only one-fifth of the growth is due to rural-to-urban migration?
Answer:
According to the paragraph given, the natural growth within the urban areas is more as the expansion is going on around the cities and towns. When a city or town expands the surrounding villages will be submerged in the city or town, The migration from rural areas is very less
My opinion Is that it is not common m all the cities and towns. In some cities and towns, it may be correct but m many arees the migrants are more in number. They are coming from rural areas to urban areas. They have different reasons lake livelihood, employment, childrens education, medical services for their chronic patients, dejection in agriculture and others. When all these people came to cities and towns there will be many problems
Government should take care of these problems and find solutions. Right to life is given by the constitution but it is not affordable to all. Agriculture is to be given priority and so villagers or farmers may stay there. It w be useful to increase the agro products also
Question 12.
Read the following paragraph and write your comments.
How does urban India contribute to Indias economic development? Service sector activities such as finance, insurance, real estate and business-related service activities such as transport, storage and communication contribute more than Widustrial activities. There is no major growth of Industrial output over the last few decades?
Answer:
According to the paragraph, It Is clearly understood that service activities play a crucial and vital role in economic development. The growth of industrial output is very less. It means service sector contributes more than that of the remaining sectors
My comments on this paragraph are that we should think of this situation in India Normally in an economy, there are three sectors viz, agriculture, industrial and service sectors. Many people depend upon agriculture in the past in our country but recently the scene in India is changing. the people are shifting from agriculture to other sectors, The narrator in agriculture Is gradually decreasing. All the activities mentioned in the given paragraph are increasing their services and contributing a lot in the economic development. In conclusion, I would like to say that the government should encourage agriculture and industries also
Many of the people working in service sector are in unorganized sector. They should be taken care of. If agriculture and industries are neglected, there will be new problems like shortage of good grains and other commodities
Question 13.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion.
One of the impacts of Increased urbanization is the use of materials that either do not degrade or take a long time to do so. This produces waste that has lo be disposed off. Where do we put such waste? As urban areas expand, the waste Is increasingly pushed to rural areas where they are either just dumped or taken to waste treatment plants?
Answer:
As per the paragraph given here, the effect of urbanization is in many ways. Collection and dumping of wastage and garbage has become a major issue. The expansion of urban areas is increasing day by day. The dumpng of waste leads to pollution in rural areas
My opinion on this paragraph Is that there are many reasons for migration and it leads to increasing in urbanization. Many migrants live in temporary settlements and they dont have shelters. These are not legal places where they live. So they dont come under regular dwellers of the city or town. Drinking water, milk, vegetables and other commodities shortage will be there
The major problem is disposal of waste. As It is irregular, they officials concerned dont concentrate on the increasing waste.
I suggest the officials that they arrange sufficient mechanisms to collect the waste and pollution tree programmes are to be taken up. Dunlng in outskirts of towns and cities Is not the solution but it creates new problems. The collection is to be properly managed not to pollute the surroundings
Question 14.
Feel that you are living In urban area. Write a letter to the Municipal Commissioner complaining about the urbanization problems arising due to migration and request to take necessary steps?
Answer:
Anandnagar colony.
Hyderabad.
4th August 2019,
To
The Commissioner,
Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation,
Hyderabad.
Respected sir,
I am Keshava Rao, the resident (H.No ............... ) of Mehdatnam. I would like to bring a few lines to your notice about the urbanization problems in out locality for yow kind consideration and necessary action.
In our locality, the migrant number is increasing. They are coming to the city because of their needs and problems but it leads to new problems here. Water supply, sewage and other waste disposals, transportation and pollution problems are arising. There are plastic covers on the roads everywhere. Many animals on the roads oat those covers and die.
As the garbage is increasing and it Is not properly cleaned, unbearable stench is spread. There may be a scope for different diseases. I request you to increase the number of workers and take necessary action to make
city dean so as to maintain good health in our locality.
Yours faithfully,
.............
............
Address on the envelope:
To
The Commissioner,
GHMC, Near Tank Bund,
Hyderabad-500 001
Question 15.
What happened to the migrant workers at times?
Answer:
At times, migrant workers are not paid their salaries, recruitment agents cheat prospective workers can collect more than the prescribed fees for their role in getting work for workers abroad. Employers also terminate the job contract before its expiry. change the employment contract to the disadvantage of migrant workers, pay less than the agreed salary arid freeze fringe benefits and other perks.
They often force workers to do overtime without making additional payments and deny permission to keep ones own passports. Indian migrant workers seldom lodge any complaint against their foreign employers for the fear of losing their jobs
Question 16.
Read the following paragraph and write your opinion on it.
People migrate from rural areas mainly due to insufficient employment opportunities and the inadequate income available In rural employment. People also migrate with the expectation of higher incomes and more opportunities for family members and may be better serviced. Ramaish was able to find work in the organized sector. However, most urban migrants have to work as labourers and find employment in the unorganized
sector. They could be working as hawkers, painters, repair persons, rickshaw pullers, construction labour, etc?
Answer:
According to the paragraph, the people migrate to urban areas as there is no sufficient work in rural areas. They expect high income from urban areas but they settle in unorganized sector. They also have no job security and they face many problems
My opinion is that nowadays every individual wants high income for their families. The people are ready to go anywhere for that. Some of them are going even abroad for that leaving their families also. In this context of the paragraph rural people are migrating to urban areas
They hope that they lead a good life but many of them face many problems. They are forcibly settling in unorganized sector. Some of then, dont find even daily wages. In unorganized sector they aro facing various troubles. They have no proper shelter, no food, no schooling for their children
In conclusion, I suggest the government to take care of these labourers of unorganized sector and launch new schemes for these migrants. In cities and towns they should be identified and recognized and provided with ration cards to get commodities from fair price shops
Question 17.
Read the flowing paragraph and write your opinion on it.
A large section of rural workers migrate for a short duration and particularly due to distress caused In rural areas. They are mainly agricultural labourers or marginal farmers in their place of origin and mostly belong to low income households, Dalits and adivasls?
Answer:
As per the paragraph given, It is understood that most of the labourers migrating from rural areas to urban areas are from marginalised families. Their income is low and they are SCs and STs. They como to cities and towns in distress.
My opinion is that most of the dal.ts and Adivasis have no agricultural lands, They are agricultural labourers working in others fields. When they tried no work in some peculiar seasons they migrate to urban areas. Especially the adlvas4s are still leading their lives based on the forest produce. Deforestation is going on. The forest cover is decreasing
So the Adivasis lose their opportunities of their collection. Many of other caste people of low income are also suffering the same. Irrespective of caste the poor are migrating. They are facing many problems in urban areas.
I suggest the government to take up new initiatives for the sake of these low-income groups. MNREGA programmes should be launched In the needy areas. The duties, Adivasis and other low-income groups of other castes also should be given priority and welfare schemes
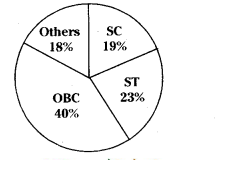
Question 18.
 Prepare a paragraph on the above pie chart?
Prepare a paragraph on the above pie chart?
Answer:
This pie chart is about the social background of short-term migrants in India. 2007- 08. It gives category-wise information of SC. ST, OBC and Others. On the overall observation, it is clearly understood that major number is from OBCs and others are less in percentage
Normally in population, the number of people from other backward classes is more. It is also observed in rural areas. People belong to scheduled castes and scheduled tribes have very less land and in some cases, they have no lands. Recently The trend is changing.
Due to some welfare schemes, they are also leading better life. The percentage of others Is also nearly equal to the scheduled castes. Their migration purpose may be different. Many of these migrants work in unorganized sector like. construction work. brick industries, selling plastic goods and vegetables or in casual work
The government should take care of these migrants arid think why these people are migrating from their places It is possible rural prosperity is to be focused. Public facilities are to be provided at the rural areas and so this migration can be stopped or decreased
Question 19.
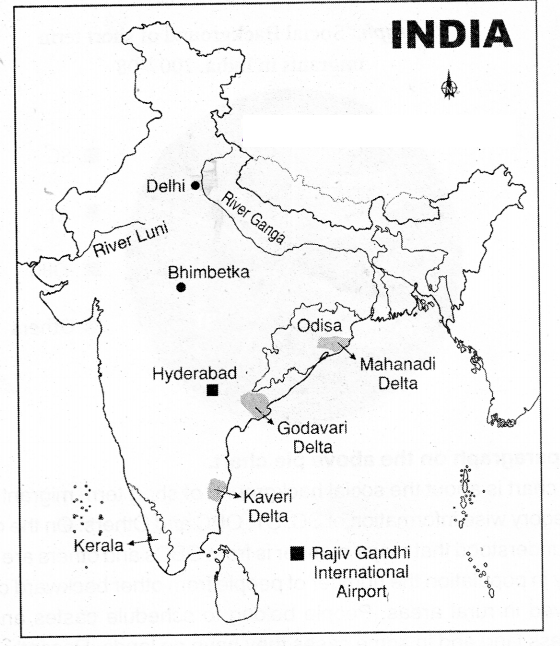
Locate the following in the given map of India?
Question 1. The only river which is flowing through the Rajasthan State?
Answer:
Luni
Question 2. The state which has Malabar coast?
Answer:
Kerala
Question 3. The state which has Utkal coast?
Answer:
Odisha
Question 4. The capital of India?
Answer:
Delhi
Question 5. Bhimbedka?
Answer:
MP (Near. Bhopal)
Question 6. Rajiv Gandhi International Ariport?
Answer:
Hyderabad